DAS:
Direct Attached Storage. Storage
(usually disk or tape) is directly attached
by a cable to the computer processor.
(The hard disk drive inside a PC or a
tape drive attached to a single server
are simple types of DAS.) I/O requests
(also called protocols or commands) access
devices directly.
NAS:
Network Attached
Storage. A NAS device
(“appliance”), usually an
integrated processor plus
disk storage, is attached to
a TCP/IP-based network
(LAN or WAN), and
accessed using specialized
file access/file sharing
protocols. File requests
received by a NAS are translated by the internal processor to device requests
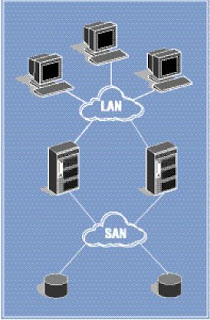
SAN:
Storage Area Network. Storage
resides on a dedicated network. Like DAS,
I/O requests access devices directly. Today,
most SANs use Fibre Channel media,
providing an any-to-any connection for
processors and storage on that network.
Ethernet media using an I/O protocol
called iSCSI is emerging in
NAS gateway:
A NAS
device without integrated
storage (i.e., just the
NAS processor). Instead,
the NAS device connects
externally to storage by
direct attachment or by SAN.





No comments:
Post a Comment